The female reproductive system is key to a woman's overall health. However, many women often neglect their reproductive health until issues arise.
Learn how regular check-ups and awareness of gynaecological conditions can help detect potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.

General Gynaecology Check-Up at Pacific Women's Clinic
The female reproductive system is key to a woman's overall health. However, many women often neglect their reproductive health until issues arise.
Learn how regular check-ups and awareness of gynaecological conditions can help detect potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
Gynaecology is a field of medicine that addresses the health of the female reproductive system. It encompasses a variety of conditions, preventive services, and treatments.
Gynaecology involves diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions affecting the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina, and breasts. Regular visits to a gynaecologist help women address any concerns and stay informed about their reproductive health at every stage of life.

Women may develop gynaecological conditions that can impact their overall well-being. Some of the most common conditions include:
Fibroids in the uterus are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can grow in varying numbers and sizes. While many fibroids are asymptomatic, some cause heavy periods, pelvic pain, and pressure. Treatments depend on symptoms and can range from monitoring to medication and surgery.
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled growths that develop on the ovaries. Although many cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, others may cause pain or complications. Treatment is typically needed for large, persistent, or symptomatic cysts.
Cervical polyps are small, benign growths that form on the cervix. They are often asymptomatic but may cause abnormal bleeding. If they cause symptoms or rule out other issues, most polyps are removed during an outpatient procedure.
PCOS is a hormonal condition characterised by irregular menstrual cycles, high androgen levels, and small ovarian cysts. It can cause symptoms like weight gain, acne, and infertility. Treatment often involves lifestyle changes, medications, and hormonal therapy to manage symptoms.
Endometriosis occurs when tissue akin to the uterus lining develops outside the uterus, causing pain, inflammation, and sometimes infertility. Treatment options include medication, hormone therapy, and surgery, depending on severity.
Cervical cancer starts in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus, and is typically caused by a persistent infection with certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). Early screening helps in prevention and treatment.
Vaginitis is characterised by inflammation of the vagina, which can result from infections, imbalances, or irritants. Symptoms include itching, discharge, and discomfort. Treatment of choice will depend on the cause and may include antibiotics, antifungal medication, or lifestyle adjustments.
Menstrual disorders encompass a range of issues, such as irregular, heavy, or painful periods. Conditions like dysmenorrhea (painful periods), menorrhagia (heavy bleeding), and amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) fall under this category. Treatments will depend on the root cause and severity.
A Pap smear is a routine screening for cervical cancer, while an HPV test checks for the presence of high-risk human papillomavirus types. Regular screenings help in the early detection of cervical cancer and HPV infections.
For more severe or persistent conditions, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include:
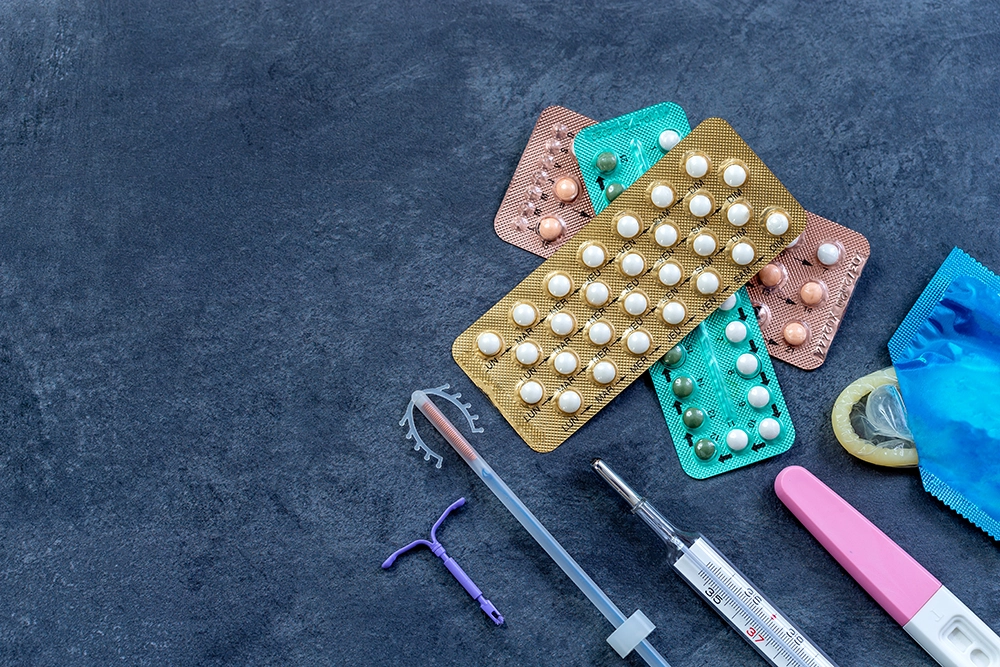
Non-surgical treatments for gynaecological conditions are essential options that can effectively manage symptoms without invasive procedures. These include:
The above symptoms may indicate underlying issues that warrant medical attention. Prompt detection and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Routine visits to a gynaecologist are essential even without symptoms, as regular check-ups can help detect potential health issues early and ensure optimal reproductive health.
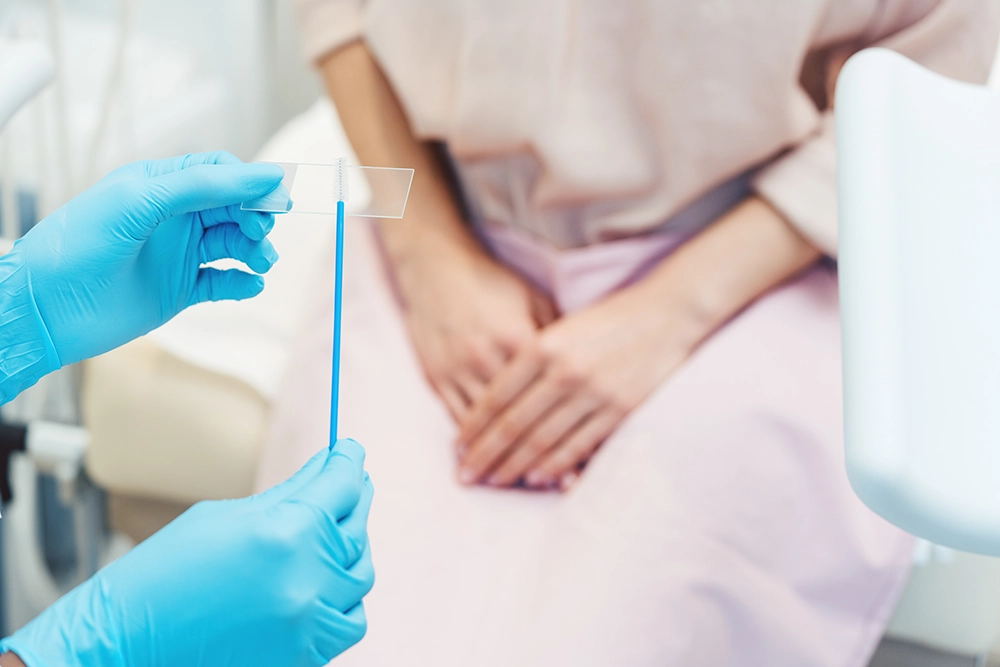
Gynaecology is essential in supporting women’s health from puberty through menopause and beyond. By staying proactive about reproductive health, women can address concerns early and maintain optimal well-being.
Pacific Healthcare Specialist Centre provides comprehensive gynaecological services to address various conditions. With our experienced gynaecologist in Singapore and modern diagnostic tools, we offer personalised care, from routine check-ups to medical treatments, ensuring that women can access the best possible care for their reproductive health.
All gynaecology consultations at our clinic are handled by Dr. Nurhidayati Binte Mohamed Suphan, our dedicated female obstetrician and gynaecologist. Dr. Nurhidayati specialises in comprehensive women’s healthcare, offering treatments for a wide range of gynaecological conditions and providing personalised obstetric care to support women through every stage of life.
Copyright © 2026 Pacific Healthcare Specialist Centre (Women's Clinic)